
Class 10 Biology | LIFE PROCESSES: Nutrition in Animals | Chapter 6 – Part 2
LIFE PROCESSES: Nutrition in Animals Q/As:
21. How do forms of nutrition differ from organism to organism?
Ans: Every organism has different adaptations and its form of nutrition differs upon the type of source (mobile or stationary) or whether the organism breaks down the food outside or swallows it as a whole and then digests it, or just takes in nutrients in without killing it and many more strategies. Each strategy decides what form of nutrition an organism will take up.
22. Describe the three types of Heterotrophic nutrition.
Ans:
PARASITIC: Derives nutrition from host cells without killing them. Eg: Lice, Tapeworm
SAPROPHYTIC: Breakdown of food takes place outside the body. Eg: Bread mould, Fungi.
HOLOZOIC: Food is swallowed as a whole and digested inside the body. Eg: Human beings, animals, Amoeba.
23. How does an Amoeba obtain its food?
Ans: Amoeba’s nutrition type is holozoic, and thus, it swallows its food as a whole and digests it. When an Amoeba senses its prey, it extends a finger-like projection called a pseudopod, which surrounds the food particle, encloses it, and the particle is diffused into the Amoeba. Then, it digests the particle inside the food vacuole and the waste material is thrown out. This engulfing of food is called endocytosis.
24. What are the two types of endocytosis?
Ans: The two types of endocytosis are- phagocytosis (phago-solid material) and penocytosis (peno-water).
25. How is a leaf adapted for photosynthesis?
Ans:
- The leaf has a large surface area for absorption of more sunlight.
- A leaf has lots of chlorophyll to absorb light and converts it into chemical energy.
- Stomata allows gaseous exchange to take place, i.e., carbon dioixide enters and oxygen diffuses out through the stomata.
26. Leaves of a healthy potted plant were coated with Vaseline to block the Stomata. Will this plant remain healthy for long? State reasons for your answer.
Ans: The plant will gradually die due to the following reasons:
- There will be no exchange of gases, because the stomata are blocked, and oxygen and carbon dioxide cannot be given out or taken in.
- There will be no absorption of sunlight.
- Thus, the processes like photosynthesis, transpiration and respiration will stop, and the plant will die gradually.
27. Describe the nutrition of an Amoeba diagrammatically.

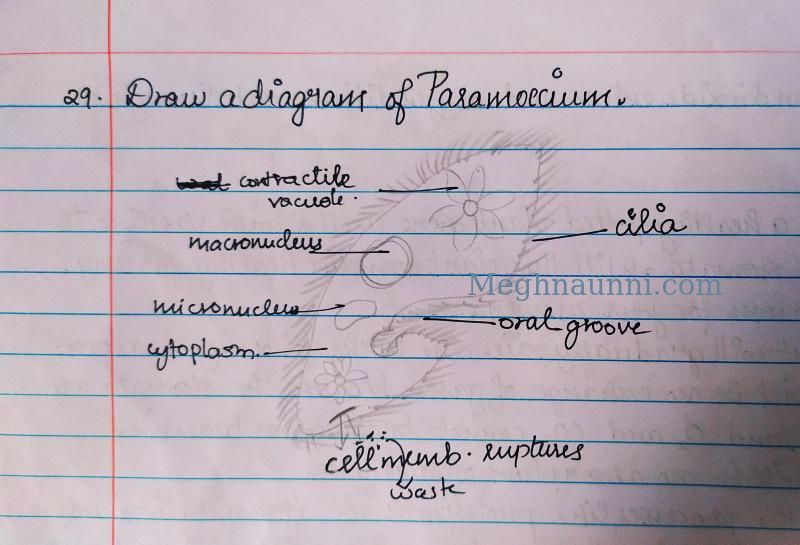
28. How is food taken in by Paramoecium?
Ans: Paramoecium is a unicellular organism and has a fixed shape. Food is taken in one spot called the oral groove and is transported to the cytoplasm where it is digested, and the waste is thrown out. The movement of the food vacuole occurs completely through cilial hair movement.
29. Draw a diagram of Paramoecium.
30. Explain the digestion process in humans.
Ans: Structure of the Alimentary Canal:
1. Buccal Cavity
2. Oesophagus
3. Stomach
4. Small Intestine
5. Large Intestine
6. Anus
1. BUCCAL CAVITY: The buccal cavity consists of the teeth, tongue and salivary glands.
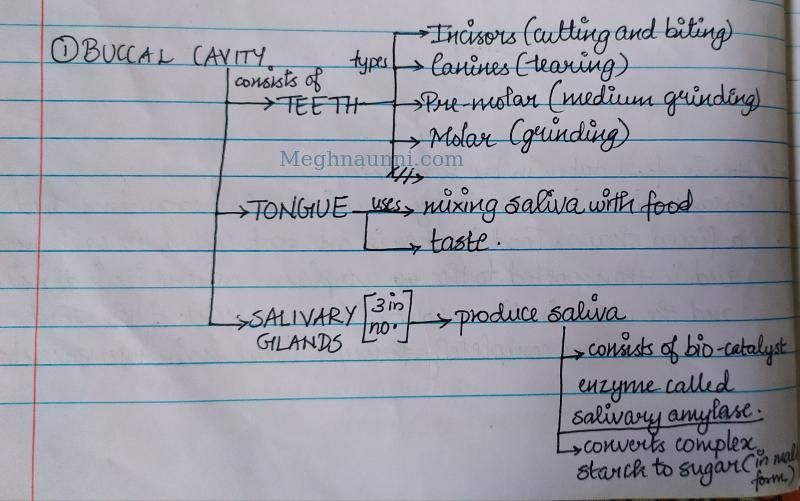
2. Oesophagus (or) Pharynx : Carries Food

3. Stomach: Large Organ which expands when food enters

Allows food to enter small intestine in small amounts (pic got cut above)
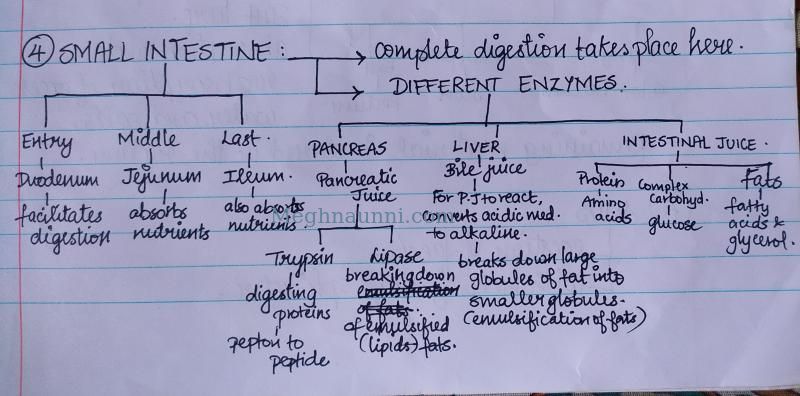
4. Small Intestine : Complete Digestion takes place here

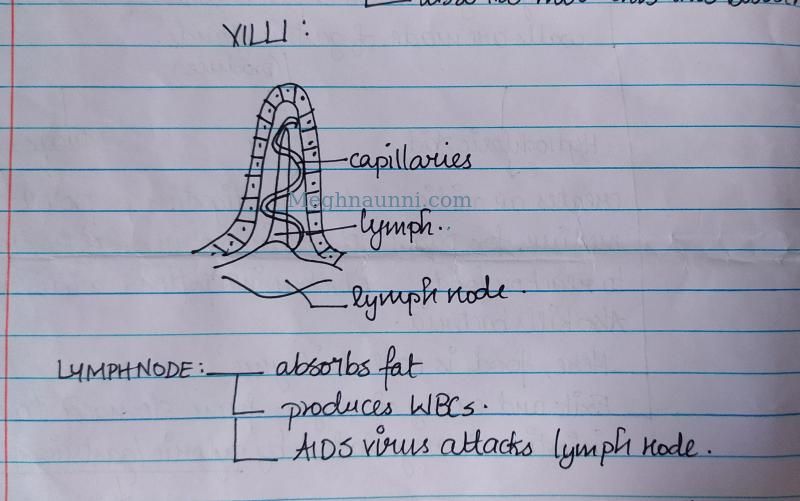
Villi & Lymphnode
5. Large Intestine:
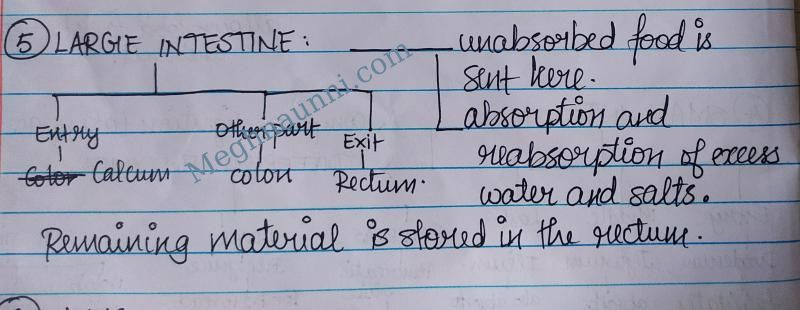
6. Anus
- Egestion of faeces
- with the help of anal sphincter
31. Why Should we brush after eating?
Ans:
- When bacteria acting on sugar produce acids that soften or demineralize the enamel, tooth decay occurs.
- When this happens, masses of bacterial cells together with food particles stick to the teeth to form dental plague.
- If brushed, the teeth will be free of acids, before the bacteria produce it.
- It prevents infection, inflammation and plague.